This article will discuss different aquaculture systems (land and water-based), feed applications under different culture systems, culture procedures, and features of different types of ponds, etc. Let’s go for details.
Any human means to improve fish production than that of the production naturally found. Man’s attempt through inputs of labor and energy to improve the yield of useful aquatic organisms by deliberate manipulation of their rates of growth, mortality, and reproduction.
Aquaculture is the farming of aquatic organisms including fish, mollusks, crustaceans, and aquatic plants. Farming implies some form of intervention in the rearing process to enhance production such as regular stocking, feeding, protection from predators, etc. Farming also implies individual or corporate ownership of the being cultivated (FAO,1988).
Aquaculture is the water farming activity where some sorts of controls (mostly based on environmental principles) are exercised over the organisms and environment to earn profit. (Grover et al. 2000)
Related article: What is aquaculture? principles, systems, and management
Compare the different cultural systems
| Culture System | Pond Preparation | Stocking density | Fertilizer application | Feed application | Water/oxygen supply | Fish harvesting |
| Extensive system | Weed fish and aquatic weeds are not removed | Uncontrolled | No fertilizer is applied | No fish feed is applied from external resources | No oxygen is supplied | Irregular harvest |
| Improved extensive system | Weed fish and aquatic weeds are removed | Semi controlled | Fertilizers are applied irregularly | Fish feed is applied irregularly | No oxygen is supplied | Fish harvest several times a year |
| Semi-intensive system | Weed fish and aquatic weeds are removed | Controlled | Fertilizers are applied regularly | Fish feed is applied regularly | Oxygen is supplied if necessary | Fish are partially harvested with irregular restocking several times a year |
| Intensive system | Complete removal of weed fish and aquatic weeds | Controlled with high stocking density | No fertilizer is applied | Balanced diet feed is applied | Full-time arrangement for oxygen supply | Fish are partially harvested with regular restocking several times a year |
Feed application under different culture systems:
| Fish culture management system | Requirement of natural food (%) | Requirement of supplementary/balanced food (%) |
| Extensive system | 100 | 0 |
| Improved extensive system | 70 | 30 |
| Semi-intensive system | 50 | 50 |
| Intensive system | 0 | 100 |
Culturable fish species and culture procedures:
| Species | The main field of cultivation | The main intensity of cultivation |
| Katla (Catla catla) | Pond | Semi-intensive |
| Mrigal carp (Cirrhinus mrigala) | Pond | Semi-intensive |
| Rohu (Labeo rohita) | Pond | Semi-intensive |
| Walking catfish (Clarias batrachus) | Pond | Semi-intensive and intensive |
| Orangefin labeo (Labeo calbasu) | Pond | Semi-intensive |
| Stinging catfish (Heteropneustes fossilis) | Pond | Semi-intensive |
| Bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis) | Pond | Semi-intensive |
| Grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) | Pond | Semi-intensive |
| Common carp (Cyprinus carpio var. communis) | Pond | Semi-intensive |
| Silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) | Pond | Semi-intensive |
| Black carp (Mylopharyngodon piceus) | Pond | Semi-intensive |
| Mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio var. specularis) | Pond/ Paddy field | Semi-intensive |
| Pangas catfish (Pangasius pangasius) | Pond | Semi-intensive and intensive |
| Pabda catfish (Ompok pabda) | Pond | Semi-intensive |
| Java barb (Barbodes gonionotus) | Pond/ Paddy field | Semi-intensive |
| Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) | Pond/ Paddy field, cultivation in a cage | Semi-intensive and intensive |
| Giant freshwater prawn (Macrobrachium rosenbergii) | Pond/ Paddy field | Developed extensive and semi-intensive |
Land and water-based aquaculture systems
Land and water based systems are used to culture aquatic plant and animal organisms commercially which are briefly discussed below.
Land based aquaculture systems
Lagoons: are natural coastal features in which populations of fish and shellfish are traditionally found, water volume ranging from less than a hectare to several thousand hectares, and fish yield are generally low and can be increased with specific management.
Salines/salt-pans/Salinas: Traditional shallow coastal areas for concentrating and collecting salt offer an interesting resource for aquatic production yields are more typical of conventional ponds due to the adoption of certain types of aquaculture.
Reservoirs: are widely used throughout the world, and represent potential resources for fishery production through enhancement or conventional aquaculture normally sited in inland areas, particularly on river systems, size can vary from a few thousand in m3 to millions of m3 in volume.
Tanks and raceways: are mainly used in intensive operations. Tanks can be of any shape. Although round tanks may be more expensive, they are superior in terms of water flow, Waste removal, and water quality.
Larger tanks are less expensive but tank greater than 10 m in diameter are difficult to design, install and manage. In general, a diameter: depth ratio of 5 to 10:1 is desirable to ensure good cleaning. Raceways are large elongated tanks, that normally have an inflow at one end and outflow at the opposite end. Length width: depth ratio should be 30:3:1
Rice fields: are important sources of aquatic animals over large areas of Asia, the introduction of hatchery fish to rice fields appears to still be relatively localized but management and capture of wild stocks are widely practiced. The Rice field is modified in rice-fish culture to encourage fish. Usually, a trench or ditch is dug around the field as a refuge or place of safety for fish.
Ponds: are normally supplied with gravity or tidal flow water supplies. Generally, ponds are cheap and technologically simple and are still the widest structure for commercial aquaculture. Major pond site requirements are given below.
- Sight level- high enough for drainage and low enough for economical water supply;
- Exposure- well exposed to sunlight, sufficient for good local water mixing;
- Soil condition- suitable for pond construction, good fertility, avoiding acidic conditions;
- Water quality- Suitable for rearing, good growth, reduced risk;
- Land cost- low purchase or lease price;
- Access- reasonable access to road and/or water for construction and operation; and
- Services- reasonable access to power supply, phone, labor freshwater, or alternatives available. Pond uses are found to be varied with deaths.
Pond depth (m):
- 0.2 to 0.5: “Warming ponds” for spawning fish early or fry rearing ponds
- 0.3 to 0.7: “kitchen ponds” for high productivity algal production
- 0.8 to 1.2: typical production pond depths
- 1.0 to 1.8: deeper ponds for overwintering
- 1.5 to 3.0: typical reservoir ponds are also used for aquaculture
Major features of different types of ponds

| Type | Major features | Applications/limitations |
| Barrage | built across suitably shaped Valleys; shape and size depend on topography | water storage, extensive stocking aquaculture, cage culture in deep ponds, and generally poorer stock/management and poorer yield. |
| Diversion | built-in suitable locations with well-controlled water supply, normally rectangular shape, size typically 100 to 5000 m2, depth 1 to 2 m. | most forms of freshwater aquaculture can be operated and managed efficiently for good yields further increased with aeration, water flow, etc. |
| Sunken | Size typically 100 t0 50,000 m2 depth 1 to 5 m, may need a pump for drainage | not widely use for managed systems but may have some cost advantages where sites are suitable |
| Tidal | Built-in lagoon and coastal plain areas with good tidal range, acceptable water quality, size typically 100 to 20000 m2 depth 1 to 1.5 m with a separate supply and drain canals | Mainly for shrimp and marine fish increasingly using pump-assisted water to maintain water quality and productivity |
| Pumped | Usually above ground, regular shape, size typically 100 to 5000 m2 | Normally for the more intensive system where the value and importance of environmental control justify the use of pumps |
| Mixed | designed for a high degree of environmental control size typically 1000 to 2000 m2, depth 1 to 3 m, with a Central drain | for experimental high value, high-intensity production only |
Water based aquaculture systems

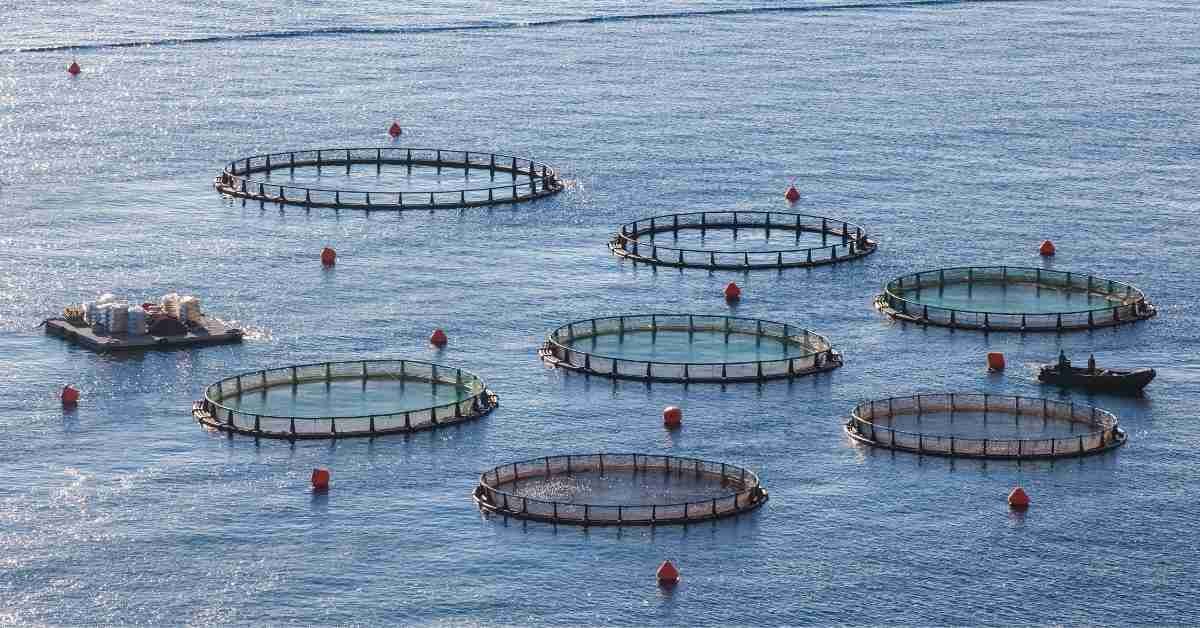
Cages: are the most versatile and cost-effective units used for aquaculture operations. Both floating and fixed cages are used. In general, fishes are stocked at high density for farming in cages. Sufficient water flow is one of the important considerations for the cage system to remove waste from the cage area.
Some advantages of cases are relatively low cost, simple and fast to assemble, not too dependent on land availability, easy to move and relocate if needed not require water supply installation, and relatively easy to service.
Enclosures/pens: are aquaculture systems in which a section of coastal or open water is separated by a solid or open screen wall or fence to create a partially controlled internal volume suitable for holding and rearing stock. Unlike cases, they do not have a separate floor that holds the stock above and is separate from the Sea, lake, or reservoir bed. The basic criteria in selecting a site for enclosures are that sufficient water exchange is available.
Potentials of aquaculture
- Food security (Important food item rice and fish as a culture, cheap source of animal protein-60%; hidden hunger >55% of the total fish production annual per capita fish intake of 21.90 kg against the requirement of 23 kg)
- Nutrition security (Source of multi nutrients, macro and micronutrients protein to a building block, minerals and vitamins to disease prevention, omega 3 fatty acid to keep the health/heart good condition, malnutrition; under nutrition; child, lactating women and poor/extreme poor people)
- Employment generation/livelihood development (involvement of >12% people; producers, hatchery/nursery operators, fishers, GO-NGO officers/staff; public-private sectors)
- Enterprise development (series of actors, input traders-seed, feed, fertilizer, chemical, medicine, producers, processors, market players)
- The utilization of resources (pond, ditches, tanks, canals, rivers, floodplain, rice land, etc.)
- National income (GDP- 3.50%; one-fourth of agricultural GDP, comparable Aquaculture GDP with other countries)
- Export earnings (fish, prawn, crab, frozen/processed food; 1.23 % of the total export earning)
- Scope water resources (ponds, ditches, tanks, canals, floodplain, rice fields, river, lakes, back swamp, sea); farmers/fisheries; unemployed youth
Problems of aquaculture
- Lack of quality seed (inbreeding)
- Lack of low-cost quality feed (40-70% of the total cost inappropriate protein level)
- Lack of inducing agents (PG, HCG, RHA, LH)
- Water quality going bad (low water depth, pH in fluctuation, insufficient DO, high turbidity, harmful gas production)
- Lack of region-specific aquaculture (variation in soil-water quality in different agroecological zones recommendation of the same package)
- Social problem (multiple ownership; short-term/poor owner-operator agreement for multiple/leased waterbody; poaching poisoning; no easy access by the poor/extreme poor to waterbody especially to the public ponds/canals)
- Economic problem (credit/capital)
Risks of aquaculture
- Unavailability of inputs
- Unavailability of labor
- Price fall of harvested fishes
- Natural calamities (drought, flood)
- Occurrence of disease/parasites)
