What is agriculture? Agriculture can be defined as the production of crops and livestock. The practice of agriculture is important to the economy of every country. It provides food and fiber for the population, and it also produces goods and services that are used in other industries.
Agricultural products are sold domestically and exported to other countries. In this blog post, we will discuss the definition of agriculture, its importance to the economy, and the role it plays in society. Stay tuned!
Agriculture definition
Agriculture is the production of plants and animals for the welfare of human beings by utilizing nature’s resources. Its primary function is to provide materials for food, cloth, and shelter to man and feed the animal.
The term agriculture has been derived from the Latin words- ‘agar’ means land or field, and ‘kultura’ means cultivation. The Greek’ geoponic’ (cultivation in the earth), ‘hydroponic’ (cultivation in water), and `aeroponic’ (cultivation in the air) refer to the three main spheres of agriculture.
Agriculture is the most important enterprise in the world. In a true sense, it is a productive unit where the resources of nature, namely, soil, sunshine, air, temperature, rainwater, humidity, etc., are integrated into a single primary unit (crop plants or their usable parts) indispensable for human beings.
Secondary productive units, livestock, birds, and insects (including fisheries) feed on these primary units and provide concentrated products such as meat, milk, wool, hide, eggs, honey, silk, and lac.
Importance of agriculture
Agriculture provides us food, feed, fiber, fuel, furniture, fertilizer, raw materials, feed-back materials for and from factories, funds, flood control, a free, fair, and fresh environment, abundant food driving out famine and friendship, and eliminating fights. It also considers employment generation, economics, education, ecology, energy consumption, use of the equipment and earning for production, protection, processing, consumption, preservation, and war against waste, transport, and trade.
Even though agricultural commodities are primarily seasonal, bulky, and perishable, they help the nation earn and conserve a more significant amount of foreign exchange and build up the national economy.
Satisfactory agricultural production brings peace, prosperity, harmony, health, and Wealth to individuals of a nation by driving away distrust, discord, and anarchy. It helps to elevate the community consisting of different castes and communities to a better social, cultural, political, and economic life.
Agriculture consists of growing plants and rearing animals to produce; thus, it helps maintain biological equilibrium in nature. It assembles the interaction of all environmental factors, namely, water, heat, light, air, and soil, distributed in the different spheres such as the lithosphere, pedosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and photosphere.
Agriculture helps to meet the basic needs of humans and their civilization by providing food, clothing, shelter, medicine, and recreation. In addition, their eyes and minds are soothed by dynamic changes from grey (bare soil) to green (growing crop) to golden (mature crop) and gay harvests.
Role of agriculture in the economy of the US
In 2020, agriculture, food, and associated industries contributed $1.055 trillion to the U.S. GDP. Farm output provided $134.7 billion—0.6% of GDP. Agriculture contributes more than 0.6% to the GDP because other industries rely on agricultural inputs. Food and beverage manufacturing, retail, food service, eating and drinking establishments, textiles, clothes, leather products, forestry, and fishing are agriculture-related industries.
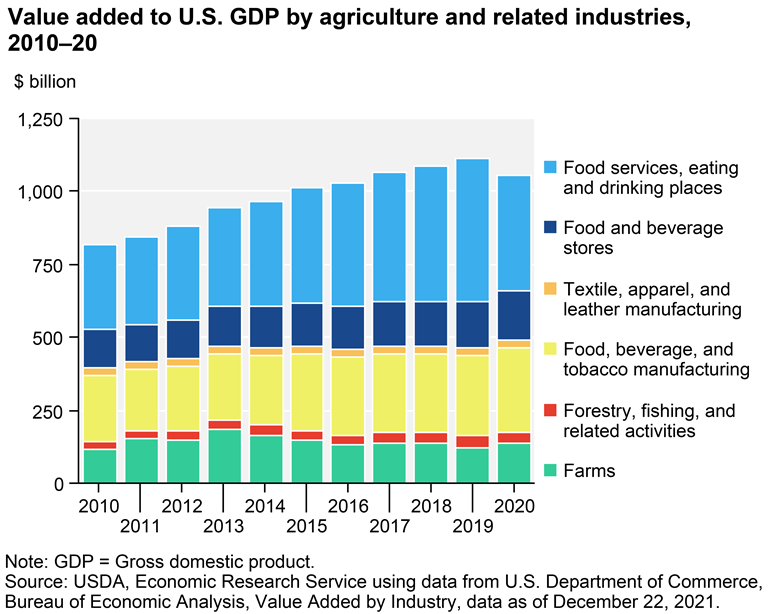
In 2020, agriculture and food accounted for 10.3% of U.S. employment or 19.7 million full- and part-time jobs. About 2.6 million of these jobs, or 1.4% of U.S. employment, were on farms. Agriculture and food industries added 17.1 million jobs. Foodservice, eating and drinking venues provided 10.5 million jobs, and food/beverage retailers 3.3 million. Agriculture-related businesses gained 3.3 million jobs.
The United States is a major producer of agricultural goods, ranging from wheat and corn to livestock and dairy products. The nation’s farmers play a vital role in ensuring that Americans have access to safe and affordable food. In addition, the agriculture industry is a significant contributor to the economy, generating billions of dollars in revenue each year.
The United States is also a major exporter of agricultural products, providing food for people around the globe. The agriculture industry has faced challenges recently, including droughts, floods, and trade disputes. However, the sector remains an integral part of the American economy and plays a vital role in feeding the world.
Role of agriculture in the economy of the UK
Agriculture is a vital part of the UK economy, contributing over £110 billion each year. The sector employs over 3 million people, and is a major export earner, with food and drink exports worth over £22 billion in 2018. Agriculture also plays an important role in environmental stewardship, with farmers managing around 70% of the countryside.

In 2021, UK farm income was £5,998 million, up £756 million (14.4%). Despite rising expenses in 2021, total livestock and agricultural outputs grew, resulting in the third-highest real Total Farm Income since 2000.
In 2021, agriculture contributed £11,222 million (0.51% of GDP) to the UK economy. This is an 8.9% rise from 2020.
2021 livestock production was £16,285 million, a 6.8% rise over 2020. All main livestock outputs witnessed price gains, except pigmeat, which fell £38 million. Milk grew by £344 million and beef by £310 million.
In 2021, crop output rose by £1,802 million (19.9%) to £10,876 million. Wheat’s value grew by £1,160 million due to high pricing and favorable growth conditions. Fruit and potatoes lost £123 million and £119 million, respectively.
Intermediate consumption rose by £2,044 million (12.2%) in 2021. Animal feed cost £978 million more and fertilizers cost £559 million more in 2021. In 2021, seed costs declined by £87 million after surging in 2020.
In recent years there has been an increasing focus on sustainable agriculture, with initiatives such as the introduction of buffer zones to protect waterways from agricultural runoff. As the world population continues to grow, there is an ever-increasing demand for food, making agriculture a vital sector for the UK economy.
Role of agriculture in the economy of China
Agriculture plays an important role in the economy of China. The country’s large population means that there is a huge demand for food, and the agricultural sector employs a significant proportion of the workforce. The main crops grown in China are rice, wheat, maize, vegetables, and fruits. The country is also a major producer of tea, silk, and tobacco.
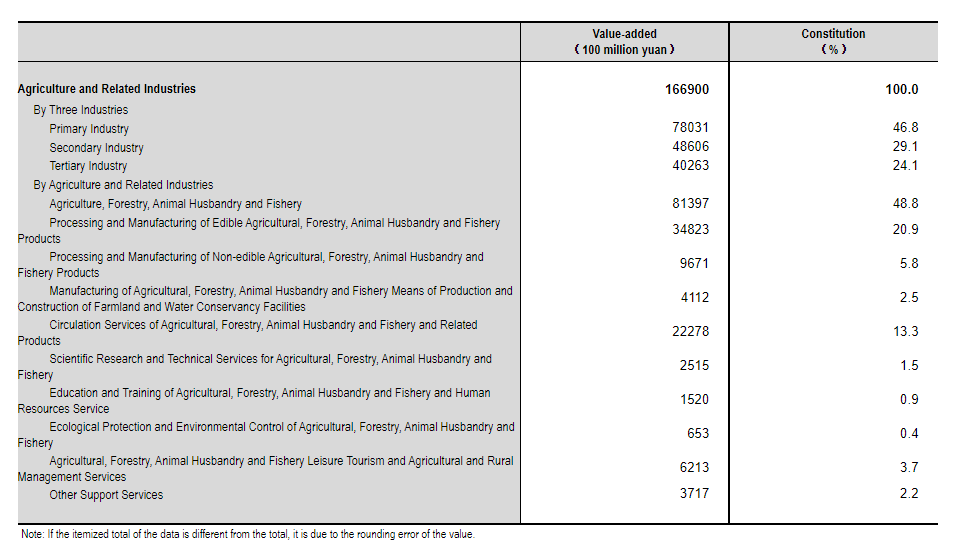
In recent years, the Chinese government has invested heavily in the agricultural sector, with the aim of increasing production and making the country self-sufficient in food. This has resulted in productivity gains and a significant increase in exports. The agricultural sector is therefore a vital part of the Chinese economy and is likely to continue to play a key role in the country’s development.
Role of agriculture in the economy of Bangladesh
The economy of Bangladesh is primarily dependent on agriculture. About 84 percent of the total population lives in rural areas and is directly or indirectly engaged in various agricultural activities. The agriculture sector plays a significant role in the country’s economy, accounting for 31.6 percent of total GDP in 1997-98 at constant (1984-85) prices.
The agriculture sector comprises crops, forests, fisheries, and livestock. Of the agricultural GDP, the crop sub-sector contributes 71 percent, forest 10 percent, fisheries 10 percent, and livestock 9 percent. The sector generates 63.2% percent of total national employment, which crop sectors share is nearly 55 %. Agricultural exports of primary products constituted 10.4% of the country’s total exports in 1997-98. In the past decade, the agriculture sector contributed about three percent per annum to the annual economic growth rate.
The agriculture sector is the single largest contributor to income and employment generation and a vital element in the country’s challenge to achieve self-sufficiency in food production, reduce rural poverty and foster sustainable economic development. The Government has therefore accorded the highest priority to this sector to enable the country to meet these challenges and to make this sector commercially profitable.
