Alley cropping is a sustainable agriculture practice that helps to conserve soil and water. Crops are planted in narrow rows between trees or other tall plants. This arrangement creates shaded areas where the soil stays moist and cool. The crops also benefit from the natural fertilization that occurs when the leaves and fruit of the trees fall to the ground.
Alley cropping
Alley cropping is the cultivation of food, forage, or specialty crops between rows of trees. It is a larger version of intercropping or companion planting conducted over a longer time scale. Alley cropping can provide profitable opportunities for row crop farmers, hardwood timber growers, nut growers, and Christmas tree growers.
Or, Alley cropping is a farming system in which arable crops are grown in alleys formed by trees or shrubs established mainly to hasten soil fertility restoration and enhance soil productivity.
Or, Alley cropping is a type of agroforestry where crops are grown in rows between strips of perennial trees or shrubs. This type of farming is thought to improve soil health and provide complementary benefits to the crops, such as shade, nitrogen fixation, and pest control. Alley cropping has been shown to be an effective way to increase crop yields and improve soil quality in tropical environments.
Or, Alley cropping is a sustainable agriculture technique that involves growing crops between rows of trees. This technique can improve soil health, provide shade and wind protection for the crops, and help to reduce erosion. Alley cropping is a complex agricultural technique that has many benefits for farmers and the environment.
Objectives of Alley Cropping
The main objective of alley cropping is to get green and palatable fodder from hedgerows in the dry season and produce a reasonable quantum of grain and Stover in the alleys during the rainy/cropping season. Some others are given below.
- To reduce soil erosion when it is established in sloping areas, thereby improving water quality.
- To improve crop performance from the increased soil productivity from the added organic matter and the microclimate created from the crop and tree shading effect. From the improved shading, water use efficiency by plants increased.
- To reduce the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Weeds are better controlled, and the increased nutrient flow improves soil fertility without fertilizers.
- To minimize nitrogen leaching hence improving water quality. The deeper tree root systems often capture nitrogen leached beyond the cropping root zone.
- To promote biodiversity.
- To maximize the use of the land.
Types of Alley cropping

Three versions of the alley cropping system, based on different objectives, are
- Forage alley cropping.
- Forage cum mulch alley cropping.
- Forage cum pole alley cropping.
In all three systems, crops are grown in the alleys, and forage is obtained from the lopping of hedgerows. Two components from an essential part of the system are;
- At the hedge rows,
- The crop is grown in the alley.
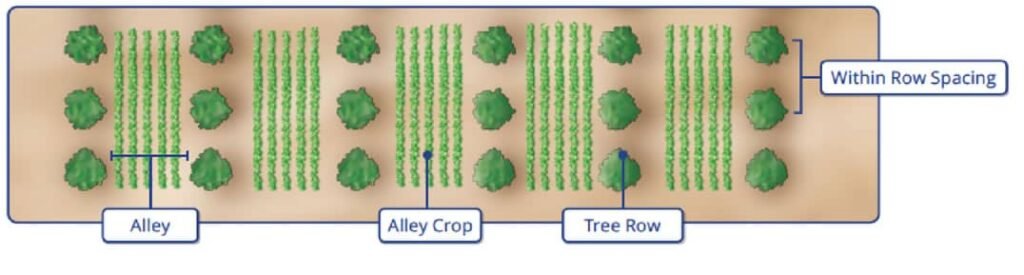
Design of Alley Cropping System

Before beginning this endeavor, a landowner must consider a few things.
- Amount of rainfall.
- Compatibility of trees and shrubs with crops to make sure competition for water, nutrients, and light is minimized.
- Spacing between and within rows.
- Sun Direction.
- Maintenance requirements & available equipment.
Benefits/Advantages of Alley Cropping
Crops grown in alleyways between rows of trees or hedges can provide multiple benefits for farmers. Alley cropping can help to reduce soil erosion, increase the yield of cash crops, and improve the overall health of the farmstead. In addition, alley cropping can also provide shade and wind protection for livestock.
- Income diversification: Crop production during the years before nut trees come into bearing or hardwood timber is harvested creates cash flow and diversifies farm income, thereby improving the return on longterm investments in trees.
- Marginal land improvement: By planting rows of nut or timber trees on land where annual crop production is low due to erosion or other limitations, marginal croplands may be converted to higher-value woodlands.
- Shelter: Rows of trees reduce wind speed, thereby controlling wind erosion.
- They also create sheltered microclimates that improve the yield and quality of crops growing in the alleys.
- Wildlife: Alley cropping increases the biodiversity of cropland which creates new habitat for wildlife.
- It provides higher total biomass per unit area than arable crops alone.
- It utilizes off-season precipitation which otherwise would go waste.
- It provides green fodder during the lean period of fodder availability.
- It provides additional employment opportunities during the off-season.
- When planted along the contours on sloppy land, it provides a barrier to run-off water holds the silt, and conserves moisture.
Alley cropping is a sustainable agriculture practice that involves the planting of trees or other perennial plants in rows between crop rows. Alley cropping can help to improve soil health and provide other benefits to crops.
In conclusion, alley cropping is a great way to improve soil health and increase crop production. It is a simple, cost-effective way to improve your farm or garden. If you are interested in trying alley cropping, please consult an expert to learn more about the best way to implement this practice on your property.
