If you’ve ever thought about having your own beehive, now is the perfect time to start. Beekeeping is a rewarding hobby that offers many benefits both for bees and people. From producing their delicious honey to pollinating our crops and other vital plants, bees are an integral part of our eco-systems – so taking up beekeeping helps us all! In this blog post, we’ll take a look at what it takes to become a successful beekeeper. We’ll cover topics such as hive management techniques, tools basics and more that will set you on the path towards becoming a successful apiarist! So let’s get started -Let’s explore everything there is to know about beekeeping!
Introduction to beekeeping
Bees are flying insects that resemble wasps and ants. They are well-known for making pollination possible and producing honey. The scientific name of the honey bee is Anthophila. Beekeeping, also called apiculture, means the care and management of honeybee colonies. Honey bee biology, lifecycle, beekeeping techniques, tools, equipment, and overall management are the basic facts you should know before starting beekeeping. In this article, we’ll discuss them.
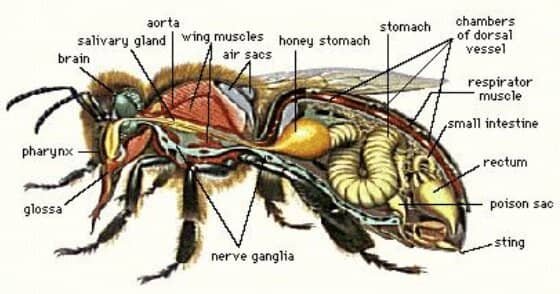
Honey bee biology
- Glossa
- Pharynx
- Brain
- Salivary gland
- Aorta
- Wing’s muscles
- Air sacs
- Honey stomach
- Stomach
- Chambers of the dorsal vessel
- Respirator muscle
- Small intestine
- Rectum
- Poison sac
- Sting
- Nerve ganglia
Life cycle of honey bee
There are 4 stages are found in the honey bee life cycle which is as follows-
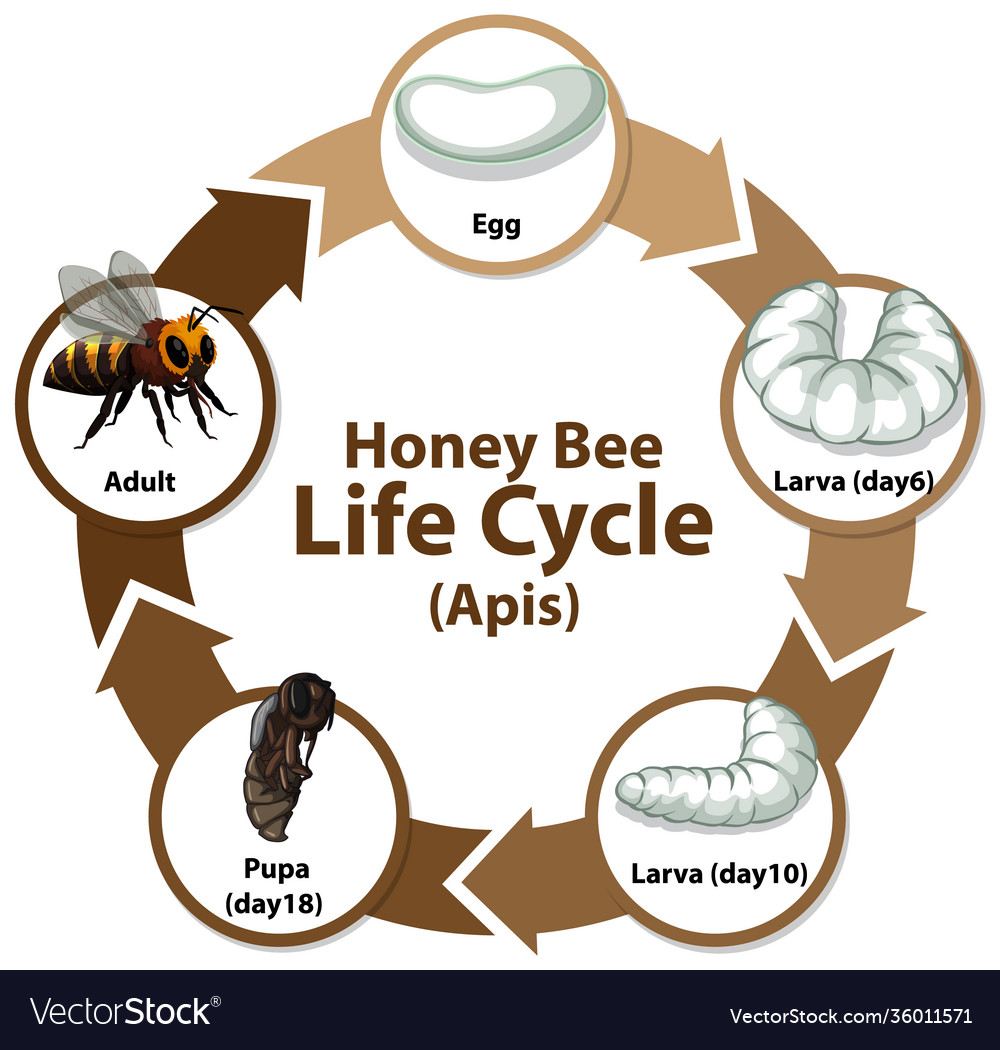
- Egg
- Larva
- Pupa
- Adult
Beekeeping techniques and management
The beekeeping technique involves the following stages:
- Preparation of bee box
- Catching a swarm.
- Hiving a swarm.
- Colony inspection.
How to choose an ideal beekeeping site?
- The selected site should be dry without dampness. High relative humidity (RH) will affect bee flight and the ripening of nectar.
- Clean natural or artificial sources of water should be provided.
- Trees serve as wind belts in cool areas.
- Hives can be kept under the shade of trees, or artificial structures should be constructed to provide shade.
- Plants that yield pollen and nectar to bees are called bee pasture and forage. Such plants should be plenty around the apiary site.
Beekeeping equipment/beekeeping tools/beekeeping kit
- Thin & thick beekeeping brushes
- SS knives
- SS & iron hive tools of L shaped & curved shaped
- Food graded plastic
- Made queen cage
- Queen gate
- Hive gate
- Honey Extractor
- Smoker
- Queen Excluder
- Pollen Trap
- Propolis Strip
- Royal Jelly production & extraction Kit
- Queen rearing kit
- Bee venom Collector.
Management of honey bees for pollination

- It is recommended to place hives very near the field to save bee’s energy.
- It is recommended to migrate colonies near the field at 10 % flowering.
- It is recommended to place colonies at 3 per ha for Italian bees and 5 per ha for Indian bees.
- The colonies should have at least 5 to 6 frame strength of bees, sealed brood, and a young mated queen.
- Should allow sufficient space for pollen and honey storage.
Pests and diseases in beekeeping
- Pests: Wax moths, Ants, Wasps, Wax beetles, Birds, Tracheal Mites, The parasitic mite Varroa destructor, Bee mites, Brood mite are the common pests found in honey bee farming.
- Diseases: Nosema Disease, European foulbrood disease, American Foul Brood, Sacbrood disease (SBV), Thai sacbrood virus (TSBV), Chalkbrood disease, and stone brood disease are the major diseases found in the honey bee farming.
Harvesting of honey bee products
Honey, Bes Wax, Royal Jelly, Bee Venom, Propolis & Pollen are the main bee products. Honey should be harvested at the end of a flowering season. In traditional or topbar hives, the beekeeper should select a comb that contains ripe honey covered with a fine layer of white beeswax, usually those nearest the outside of the nest. Honey is extracted only from super combs using honey extractor equipment.