Betel Vine Diseases Symptoms and Management: Collar rot/Footrot/Stem rot, Root rot, and Leaf spot/Anthracnose of Betel vine are the three most common types of diseases are found in betel vine.
Betel Vine Diseases
- Collar rot/Footrot/Stem rot of Betelvine
- Root rot of betel vine

1. Collar rot/Foot rot/Stem rot of Betel vine
Causal organism: Sclerotium rolfsii.
Symptoms of Stem rot of Betel vine
- The vines of all stages are susceptible to the disease.
- The infection usually starts at the collar region.
- Whitish colony mycelium is seen on the stem and roots.
- Brown-colored mustard-like sclerotia are seen on the infected stem and soil near the vines.
- The stem portion shows the rotting of tissues at the plant of attack, and the plant shows dropping of the leaves and withering, finally dry up.
Favorable condition of Stem rot of Betel vine
- A high temperature of 28-30 C.
- Organic fertilizer-rich soil and plant debris are favor for the disease.
Control Measures of Stem rot of Betel vine
- Remove the affected vines with the roots and burned.
- Apply more soil amendments like neem cake, mustard cake.
- Apply Trichoderma compost fertilizer @ 5g/plant.
- Treated vine with Provex/Bavistin @ 2g/L of water before planting.
- Drench the soil with 0.1% carbendazim.
- After founding the disease, spraying Provex/Bavistin @ 2g/L of water on foot of plant near the soil.
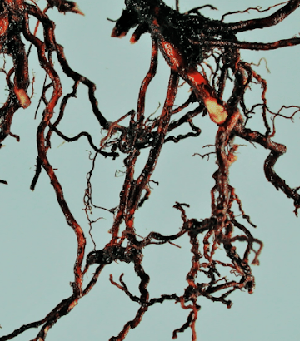
2. Root rot of betel vine
Causal organism: Rhizoctonia solani.
Symptoms of Root rot of betel vine
- Leaf pale at the primary stage of infection.
- The leaf becomes discolored and dies.
- In this time, the root shows the red color and split into a small portion.
Control Measures Root rot of betel vine
- Remove the affected vines with the roots and burned.
- Apply more soil amendments like neem cake, mustard cake.
- Apply Trichoderma compost fertilizer @ 5g/plant.
- Treated vine with Provex/Bavistin @ 2g/L of water before planting.
- Drench the soil with 0.1% carbendazim.
- After founding the disease, spraying Provex/Bavistin @ 2g/L of water on foot of plant near the soil.

3. Leaf spot/Anthracnose of Betel vine
Causal organism: Colletotrichum piperis.
Symptoms of Leaf Spot/Anthracnose of Betelvine
- The leaves show small, black, circular spots initially, which later enlarge and develop to a size of 2 cm, become concentric, and covered with a yellow halo.
- The affected leaves turn pale yellow and dry up with large black dots in the center of the spots.
- Black, circular lesions may develop on the stem, enlarge rapidly and wrap the stem resulting in withering and drying.
Favorable condition of Leaf Spot of Betel vine
- In high humidity, it spread rapidly.
Management of Leaf Spot of Betel vine
- Collect and destroy the infected leaves.
- Cultivate resistant varieties. e.g. BARI Pan 1, BARI pan 2.
- Spray with 0.2% Ziram or 0.5% Bordeaux mixture after plucking the leaves.
- Spraying Tilt 250 EC @ 0.5 mL/L of water at 23 times in 10 days intervals.
