Blast disease of rice management
Causal organism
Scientific name: Pyricularia oryzae
Occurrence/distribution of Blast disease of rice
The blast disease of rice occurs world wide and one of the most important disease of rice, particularly where rice is irrigated or receives high amounts of rainfall and high levels of N2 fertilizer.
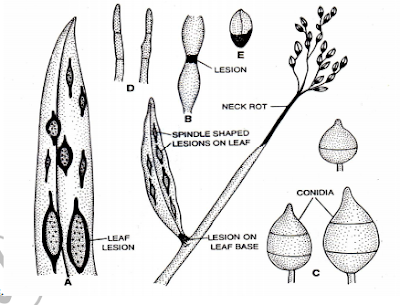
Symptoms of Blast disease of rice
Rice blast affects the levels on which it cause diamond shaped white to grey lesions with dark green to brown borders surrounded by a yellowish halo, the lesions may enlarge, coalesce and kill entire leaves. Blast also affects the leaf collar, which it may kill and the stem nodes and occasionally internodes which at heading, may results in production white panicles or breakage of the stem at the infected node. This is usually the most destructive symptom of the disease and is called the neck blast or panicle blast pathogen has been known as Pyricularia oryzae.
Recurrence of the pathogen of Blast disease of rice
The pathogen over season as mycelium and conidia on diseased rice straw or seeds. The mature conidia become air borne and on landing on rice plants . The conidia adhere strongly through a stickly mucilage . They produce at their tip . The rice blast is greatly favoured by high nitrogenous fertilizer prolonged leaf, wetness and night temperature around 20 c. ̊
Control measures/Blast disease of rice management
i. Cultivate resistant cultivars.
ii. Early planting.
iii. Keeping nitrogenous fertilizer to the minimum necessary.
iv. Spraying fungicides. i.e- mancozeb blasticidin-s, benomyle, pyroquilon and tricyclazole at the 0.2 – 0.5%.