Brown spot of rice control, causal organism, symptoms
Causal organism of Brown spot of rice
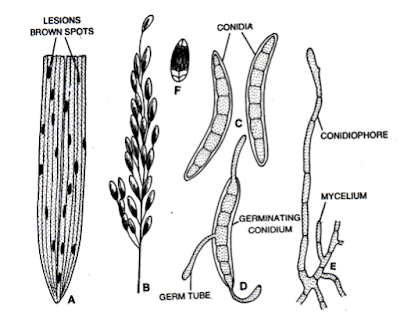
Scientific name: Helminthosporium oryzae or Bipolaris oryzae.
Distribution of Brown spot of rice
The disease has been reported from all the rice growing countries of the world.
Symptoms of Brown spot of rice
All parts of the plants are being infected except roots. Sometimes the necrotic lesions are found to the present even on the first emerging leaves. In severe cause, the seedling are blighted and become dead. The most characteristics symptoms of the disease is the development of dark brown spot on the upper surface of the leaf lamina. The spots are developed on the leaf blade and leaf sheath. The spots are various shapes and sizes. They are isolated dark-brown oval and scattered through out the leaf blade and leaf sheath. The spots developed also on leaf sheath and culm below the ear. The base of the panicle becomes shrunk and discolured. The inflorescence and individual spikelets also become infected. If the inflorescence is attacked at an early stage , it fails to develop. The grains forms inside the affectd spikelets become discoloured
Nature & recurrence of Brown spot of rice
Disease is primarily seed borned. The fungus is found as dormant mycelium in the husk and on the kernel and often it infects the germinating grain. Secondary infection is caused by air borne conidia. Generally, such conidia are produced either from primary infected plants or from other sources.
Host plant of Brown spot of rice
Wheat- Triticum aestivum,
sugercane- Sacchrum offiinalis, maize- Zea mays.
Management/Control measures of Brown spot of rice
i. Resistant varieties: Cultivation of resistant varieties BRRI-28, BRRI-29, BRRI-30, BR-3.
ii. Seed treatment: Seeds are treated with agrosan GN, organo mercurials. In 50-52ᵒc temperature for 10 minutes hot water treatment also done in severe cases.
iii. Spraying and dusting: Spraying of bordex mixture, perenox, Dihane-78 has been found to very effective.
iv. Proper manuring.