Definition and Characteristics of drought resistant plants
Definition of Drought Resistance
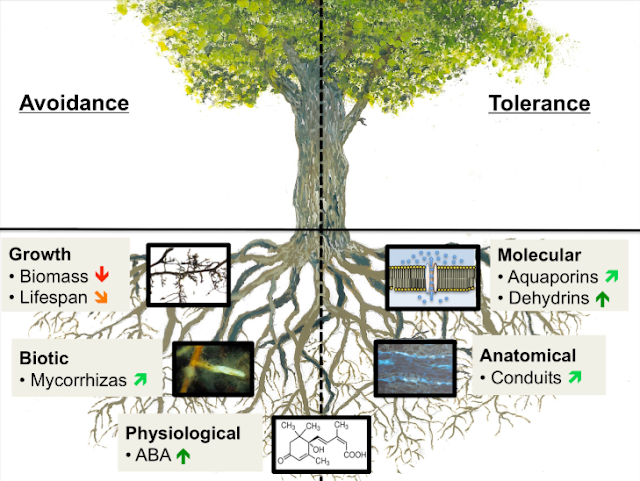
It is the ability of a plant to maintain favorable water balance and turgidity even exposed to draught conditions there by avoiding stress and its consequences. Stress avoidance due to morphological, anatomical characteristics which themselves are the consequences of the physiological processes induced by drought these zerophytic characteristics are quantitative a d vary according to environmental conditions.
A favorable water balance under drought conditions can be achieved by transpiration before a• soon as stress is experienced. These are called “water savers” or Accelerating water uptake sufficiently so as to replenish the lost water called as “water spenders”
Plant characters associated with drought resistance
|
Morphological & Anatomical
|
Grain yield; maximum root length, Root volume, Root dry weight, Root thickness, Root surface area, above ground biomass, Harvest index, Leaf drying, Leaf tip firing, Delay in flowering, Aerenchyma, Leaf pubescence.
|
|
Phenological
|
Earliness, Delay in flowering, Anthesis, Silking interval, Seedling vigor, Weed competitiveness, Photosensitivity , Perennially
|
|
Physiological & Biochemical
|
Osmotic adjustment, Carbon isotopes discrimination, Stomatal conductance, Remobilization of stem reserves, Specific leaf weight , ABA electrolyte leakage, Leaf rolling, Tip firing, Stay green, Epicuticular wax, Feed foreword response to stress.
|
|
Oxygen scavenging
|
Heat shock proteins, Cell wall proteins, Leaf water potential, Water use efficiency, Aquaporins, Nitrogen use efficiency, Dehydrins.
|
Important Agricultural Websites