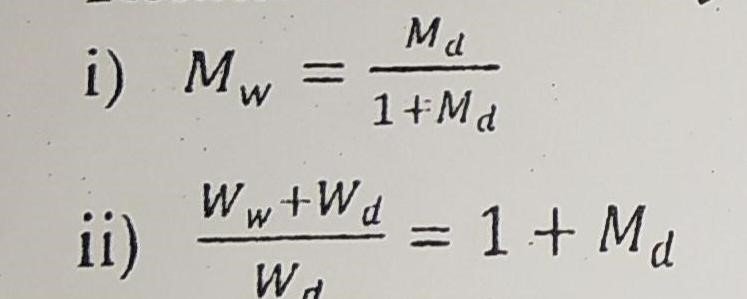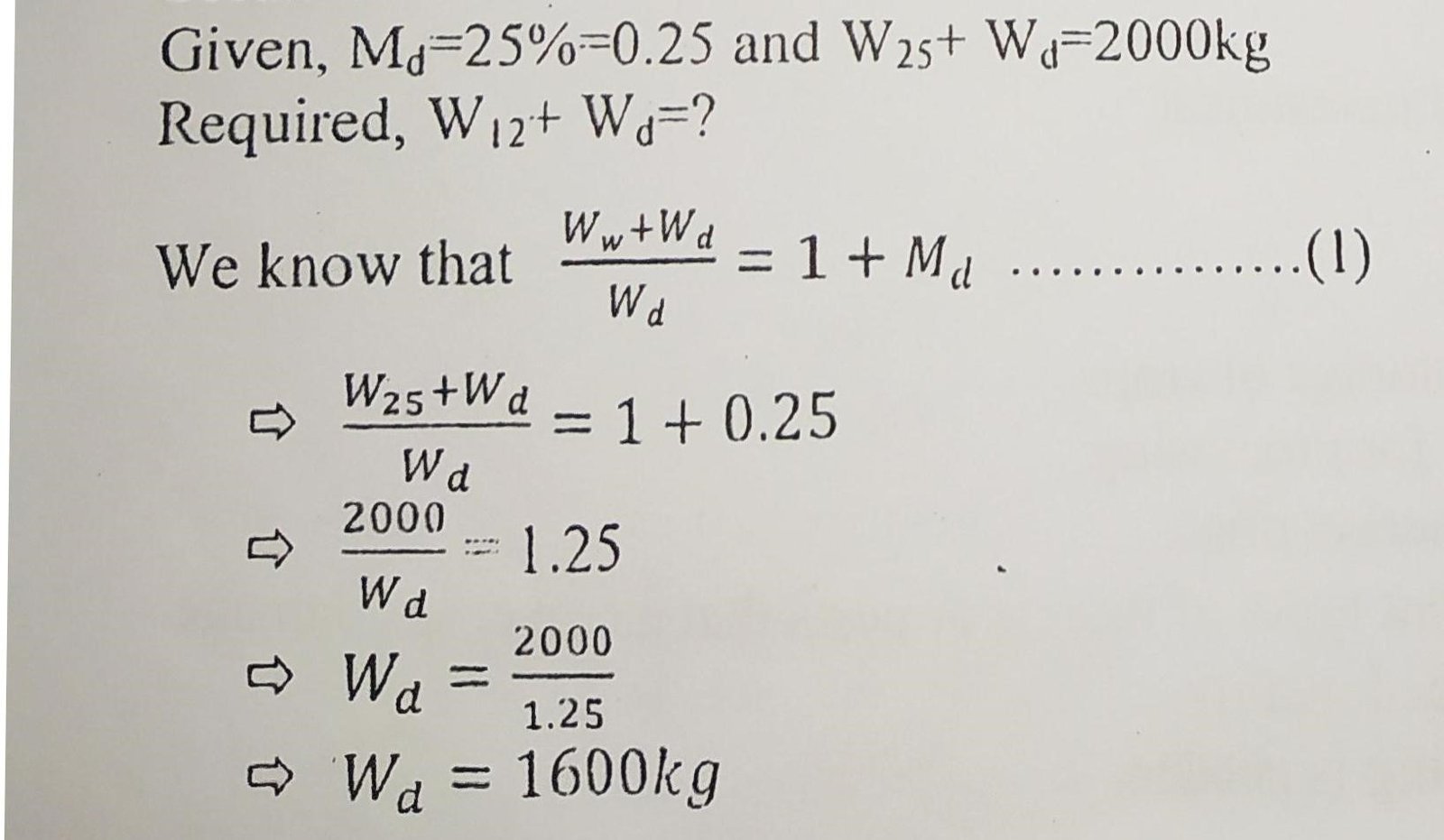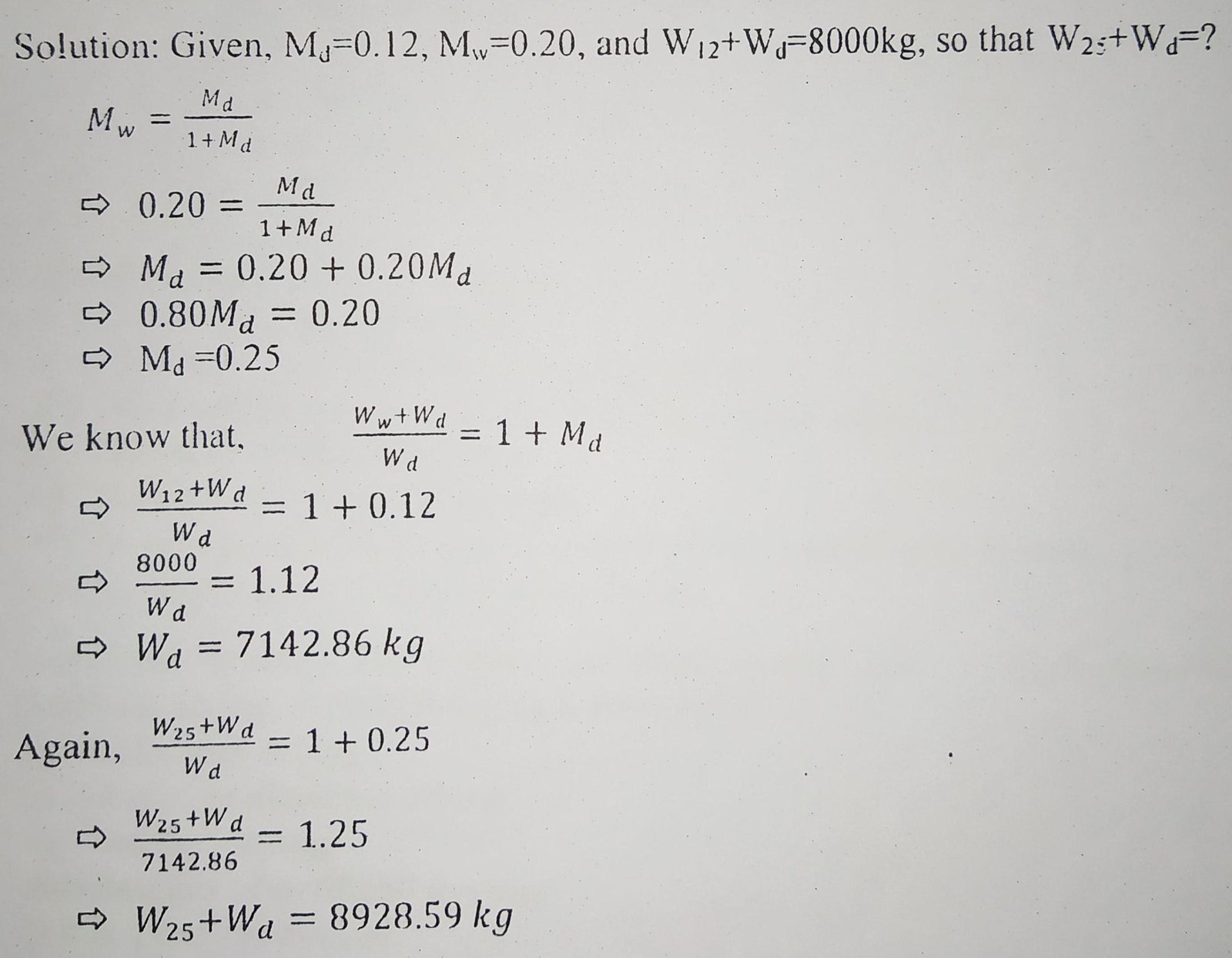Drying is the process of removing water or other solvent from a solid, liquid, or gas. It is a physical change that occurs when moisture is lost from a substance.
The rate of drying depends on the surface area of the material, the humidity of the surrounding air, and the temperature. In general, the higher the temperature and the lower the humidity, the faster drying will occur.
Drying Definition
Drying is the process of removing excess water keeping the nutritive value, speed visibility, and further use.
Drying is a process that uses heat to remove water from a material. This can be done in a number of ways, including using an oven, a microwave, or a dehydrator. When water is removed from a material, its structure changes. This can make the material harder and less likely to spoil.
Dehydration
It is the maximum level of drying i.e to keep the product until bone dry.
Classification of drying
Drying may be classified into two groups-
1) Natural drying and
2) Artificial drying
Natural drying: Natural drying means sun drying when excess water is removed by sunlight, the process is called natural drying. Natural drying is done by three ways-
- By standing crops
- By cut stock and
- In threshed grain
Advantage of natural drying
- Cost is less.
- No need skill labour.
- No need initial investment.
- It does not need any mechanical power.
- No need of any fuel.
Disadvantages of natural during
- It is an uncontrolled method.
- When sun is not available, it is not possible.
- This method require large number of unskilled labour.
- The process takes long time.
- This method requires large area.
- There is possibility to loss of crops by birds, hens or other animals.
- Normally grain did not dried uniformly.
Artificial drying: The method, in which excess water of grain removed artificially, is called artificial drying. Artificial drying is three types-
- Mechanical drying
- Infrared or dielectric drying
- Chemical drying
Advantages of artificial drying
- It is a control method.
- It can be done whenever it needs.
- Small amount of labour is required.
- It takes very short time.
- It needs a small area.
- No risks of loss of grain.
Disadvantages of artificial drying
- The method is costly.
- Needs skill labour.
- Needs a large amount of initial investment.
- Co-operating cost is required.
Purpose of drying
- Drying is needed for the future storage of crops.
- Drying makes crops favourable for processing.
- Drying is important to insure market price.
- Drying saves crops from different types of insects or pests that cause crops damage.
- Drying is essential to improve seed quality.
- To improve nutritive value, drying is needed.
Safe moisture content of some crops:
- Paddy.-12-15%
- Wheat—12-13%
- Sorghum-..-11-12%
- Soyabean—-10-12%
- Barley—-13%
Moisture content calculation
Moisture contentof grain can be calculated in two ways.
- Wet basis (wb)
- Dry basis (db)
Wet basis:
Generally the moisture content in substance is expressed in percentage by wet basis. Amount ofmoisture in wet basis is calculated by the following equation.
MCwb = Moisture content wet basis [%]Wi = Initial weightWf = Final weight
Dry basis:
Generally dry basis is used in research purpose to calculate amount of moisture. The calculation to determine the weight of moisture in dry basis is very simple and it is done as follows.
MCdb = Moisture content dry basis [%]Wi = Initial weightWf = Final weight
Relation between dry basis and wet basis
Problem no. 1: 2000 kg of freshly harvested paddy with a moisture content of 25% (dry basis) i dried to a moisture content of 12% (db). Determine the final weight of the paddy after dry.
Solution:
Hence the final weight of the dried grain is 1792 kg.
Problem no. 2: 8000 kg of paddy with a moisture content of 0.12 (db.) is required for a research project on grain storage. It was decided that the available freshly harvested paddy with a moisture content of 0.20 (wet basis) should be procured and that will be dried to a moisture content of 12% on a dry basis. How many kg of freshly harvested paddy is to be procured.
Solution:
Hence the weight of freshly harvested paddy is 8928.59 kg.
Moisture content
The moisture content of a product is a numerical value expressed in percentage. This is determined by the relationship between the weight of the water contained in a given sample of grain and the total weight of that sample:
H %=( WWater/ (Wdm+Wwater)) ×100
When: H% the moisture content of the sample (in %);
W, water = weight of the sample’s water (in kg);
Wdm weight of the sample’s dry matter (in kg).
Therefore, to say that paddy has a 25 percent moisture content means that in a sample of 100 g of raw product there are 25 g of water and 75 g of dry matter.
For example, if 200 kg of peas at 32 percent moisture content are dried to 19 percent moisture content, what is the weight of the dried peas?
Reference: