 |
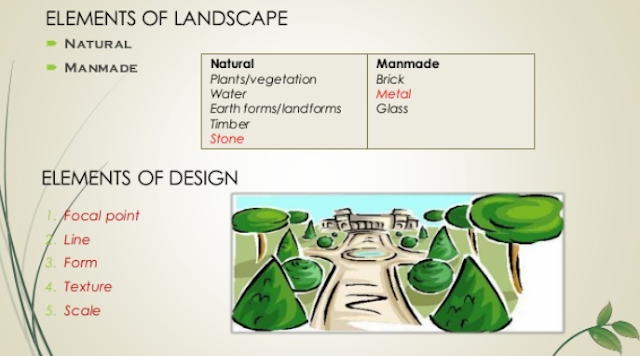
| Elements of landscape design |
Elements of landscape design
The design elements are visible features of all objects. So, these are as –
1. Color:
People respond differently to color. Certain colors – reds, oranges, and yellow are described as warm colors and appear to advance towards the viewers. Cool colors – blues and green – tend to recede in a landscape composition. The attributes of color are hue, value and intensity or chroma. Some colors are enhanced when viewed against certain background colors and other clash. Gray is a neutral color and along with a cool color such as dark blue, can create an effective background. Some colors are overwhelming and loud, and others are soft and mild. Flowering plants have a wide array of colors in their petals. Some flowers have solid colors, while others are variegated.
Choice and arrangement of colors in the landscape are critical considerations to the overall visual appeal. Flower color is strongly affected by light. Shade subdues and sunlight intensifies colors, which should be kept in mind when locating plants in the landscape.
Flowers are not the only sources of color in the landscape. Leaves, although predominantly green may have variegation and seasonal color changes in autumn. Tree bark also produce variety in color.
2. Texture:
2. Texture:
Texture design to the visual effect of tactile surface qualities. As for example, the visual difference between burlap and silk or between the surface of a pineapple and that of a rose petal.
Texture may change with the season. While a deciduous tree has its leaves, it presents a smooth texture.
However, when the leaves fall in autumn, the bare branches present a rough or course texture. Tree barks vary in texture, some being smooth and others such as oak, thick and rough.
Texture in the landscape is not limited to plants. Other materials, such as those used as mulch, have varying texture. Gravel is fine in relation to rocks, and saw dust is fine when compared with tree bark. Texture is also modified by distance.
3. Form:
Form refers to the shape and structure of a three – dimensional object (sphere, cube and pyramid). The outline of a plant against the sky, it depends on the structure and shape of the plant. For example, tree may be conical, columnar, pyramidal, and spherical and so on. Plants of different forms may be grouped and arranged in a certain fashion to create a different overall form in the landscape. For example, a landscape architect may group a number of plants with narrow columnar form to create a horizontal form. This strategy is used in creating a hedge, around a house.
4. Line:
The effect of line is accomplished through the arrangement of objects. Line is a boundary element of design, shape and structure are defined by lines. A design element line, when used effectively, has the capacity for eliciting emotional responses, making one display appear elegant and another disorganized. As indicated previously form is a three dimensional attribute, but it can be interpreted as one dimensional by line. Line is the means by which form guides the eye.
Natural lines occur in nature but often are complex. Line is a design tool that a landscape architect uses to create and control patterns in the landscape.