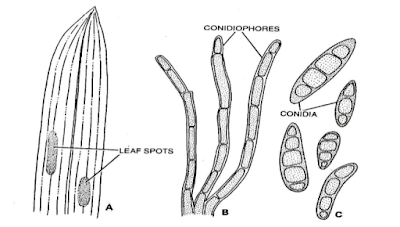
Leaf blight of maize management with its symptoms
Pathogen of Leaf blight of maize
Helminthosporium turcicum pass.
Systematic position
Class- Deuteruomycetes
Order- Moniliales
Family-Dematiaceae
Distribution of Leaf blight of maize
The disease is quite common in many parts of India. It was first described in Italy in 1876 and since then has been recorded from the United states, South Africa, Japan and the Philippines and most maize growing countries.
Symptoms of Leaf blight of maize
The symptoms appear as small, yellowish, round or oval spots on the leaves. These extends along the leaf and coalesce into longitudinal bands, which may cover a great part of the leaf. The affected tissue gradually become dark in coloured and are being covered in moist weather with velvety dark- green patches due to the fructification of the fungus. Ultimately leaves are dried up and have a blighted appearence. The plants remain stunted and the ears poorly developed.
Recurrence of disease
The disease survives on plant debris in the soil.
Leaf blight of maize management/Control measure
Chemical method: The leaf blight on maize effectively be controlled by spraying either Captan or zineb. Sanitation and crop rotation should be practiced.