Farm management is the application of economic principles in an organization and operation of a farm business. There are some economic principles applied to farm management, which are discussed below:
- The law of diminishing returns
- Cost principle.
- Principles of substitution
- Principle of opportunity cost
The law of diminishing returns
The law explains the input-output relationship known as a factor-product relationship. According to Benham, “As the rate of one factor in a combination of factors increases, after a certain point, the average and marginal product for that factor will diminish.
In other words, when various inputs are applied in a production process, if one input is added at an increasing rate, other inputs remaining constant, alter a situation at the first marginal return (MR), then average return (AR), and finally total return (TR) will diminish, which is known in agricultural economics as the law of diminishing return.
Law of diminishing returns example
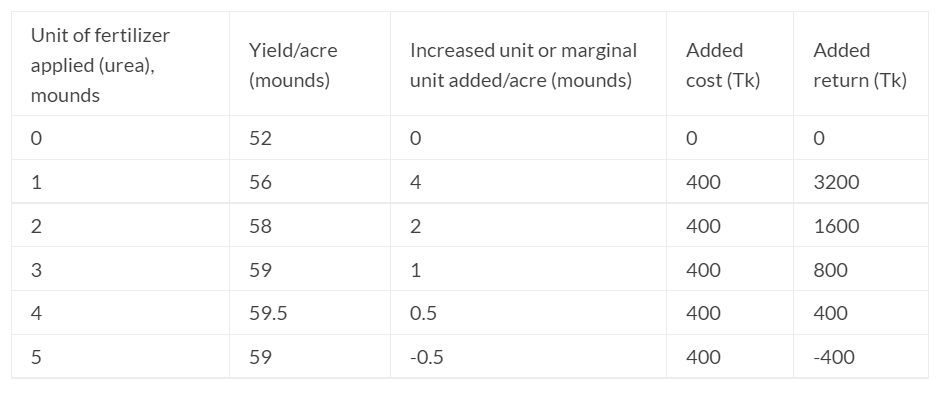
For example, to illustrate the operation of diminishing return and making a decision of the optimum dose by the operator is given below: (i) Price of urea per mound is Tk. 400, (ii) Price of rice per mound is Tk. 800
| Unit of fertilizer applied (urea), mounds | Yield/acre (mounds) | Increased unit or marginal unit added/acre (mounds) | Added cost (Tk) | Added return (Tk) |
| 0 | 52 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 56 | 4 | 400 | 3200 |
| 2 | 58 | 2 | 400 | 1600 |
| 3 | 59 | 1 | 400 | 800 |
| 4 | 59.5 | 0.5 | 400 | 400 |
| 5 | 59 | -0.5 | 400 | -400 |
This example shows that the total yield is 52 mounds when no fertilizer is used. When one mound of urea is added to the same land, yield becomes increased by four mounds. When two and three mounds of urea are successfully added to the same land, yield increases by two and one mound, respectively.
We see that the added return is in decreasing tendency, the total yield is increasing condition till four units of fertilizer dose. After this situation, if more urea is added to the land, the total return and added return decrease, which is not economical. This is the point of diminishing return.
Rule: Variable resources should be added to the fixed resource if the added return is greater than the added cost.
Application: This principle is important in specifying how large a farm we should operate or how much labor or how machinery we should add to our present unit,
This law is applicable to find out the most economical dose of any variable resource to be applied.
Diagrammatic representation: