Evapotranspiration is an important study in soil science. This article will discuss evapotranspiration definition, factors affecting ET, methods for ET determination, potential evapotranspiration, a comparison between ET and PET, etc.
Evapotranspiration (ET)
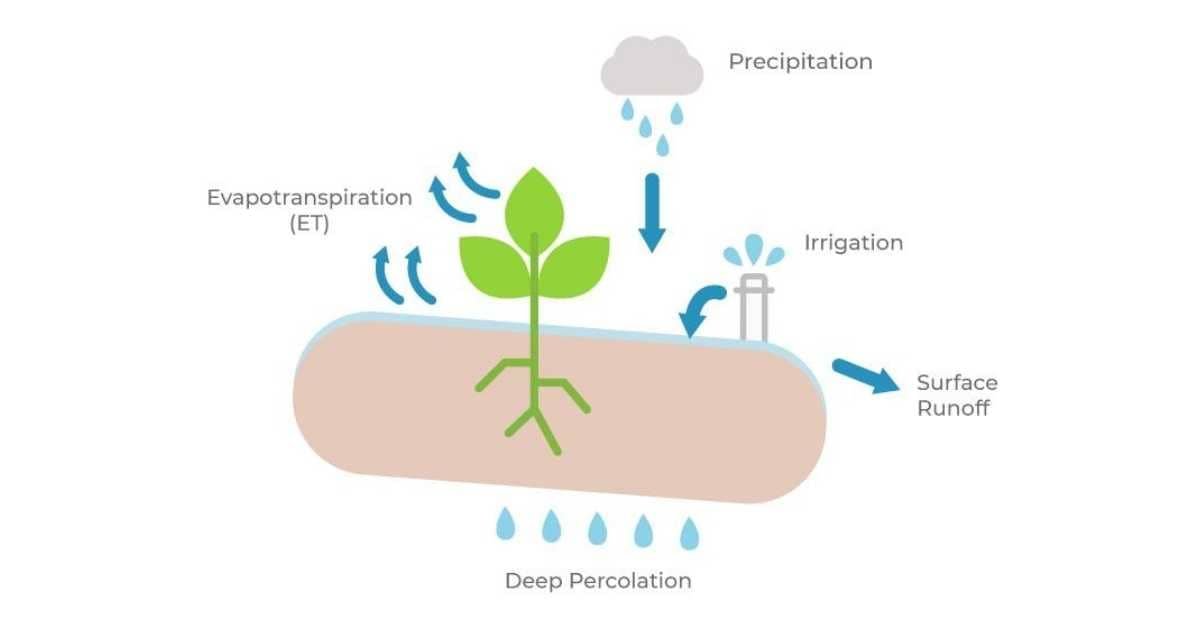
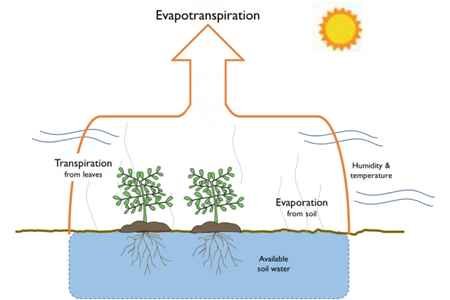
The combination of two separate processes of water loss, one by evaporation from the soil surface and another by transpiration from a plant, is called evapotranspiration (ET). It is the sum total loss of water through evaporation and transpiration.
- Evapotranspiration (ET) = Evaporation (E) + Transpiration (T)
Potential evapotranspiration (PET)
It may be defined as the maximum evapotranspiration that occurs when the ground is completely covered by actively growing vegetation and where there is no limitation of soil moisture. It may be considered the upper limit of ET for a crop in a given climate.
Usually, PET ≥ ET
At the initial stage of crops, PET > ET
At the maximum growth stage of crops, PET = ET
List the factors affecting ET
Factors affecting ET:
1. Meteorological factors
- The intensity of solar radiation
- Day length
- Air temperature
- Wind speed
- Humidity
- Cloudiness
- Precipitation
- Visibility of atmosphere – eg: fog
2. Geographical factors
- Altitude
- Latitude
- Slope
- Distinguish land and water bodies
- Topography
3. Crop factors
- Nature of crop
- Age or growth stage
- Method of cultivation
- Nature of leaf
- Nature of root system
- Nature of canopy
- Nature of stomata
- Duration of growth
- Growing season
- Crop density
- Crop variety
4. Soil factors
- Availability of soil moisture
- Soil texture
- Soil structure
- Soil temperature
- Bulk density
- Presence of plow pan
- Soluble salt content
- Water holding capacity
- Nature of pore space
- Depth of water table
- Organic matter content etc.
5. Cultural and management practices
- Tillage
- Method of cultivation – Broad casting and Line sowing
- Weeding
- Mulching
- Irrigation
- Drainage
- Application of fertilizer and pesticides etc.
What is KC? State the factors affecting KC
Crop factor (KC):
Crop factor or co-efficient may be defined as the ratio of ET over PET.
KC =ET/PET
In formal field crops, it varies from 0.2 – 1.0 except for flooded or rice fields.
In rice fields, it ranges from 0.2 to 1.3
Factors affecting KC:
- Nature of crops
- Age of crops/growth stage
- Crop variety
- Plant density
- Planting method / Method of cultivation
- Nature of canopy
- Nature of leaf
- Nature of stomata
- Nature of root system
- Growing period / Duration of period
- Crop variety
Difference between ET and PET
| ET | PET |
| The sum total of the losses of water from the soil through evaporation and transpiration is called ET. | PET may be defined as the ET that occurs when the ground is completely covered by actively growing vegetation and there is no limitation in soil moisture. |
| ET ≤ PET | PET ≥ ET |
| The ground may or may not be completely covered with vegetation. | The ground must be completely covered with vegetation. |
| ET is maximum at the maximum vegetative stage of crops. | PET is considered to be the upper limit of ET. |
Difference between Kp and Kc
| Kp | Kc |
| The variation of moisture loss between the pan and the crop field is called the pan factor and it is denoted by Kp. | The crop factor (Kc) may be defined as the ratio of ET over PET. Or, The variability of ET due to the variation of the crop is called crop factor.(Kc) |
| Kp = PETEWhere, E = evaporation | Kc = ETPET |
| Kp varies with wind speed, humidity, and distance from the crop field. | Kc varies with the type of crop and stages of growth. |
| Kp ranges from 0.40 to 0.85 | Kc ranges from 0.2 to 1.0 |
Name of different methods for ET determination
Methods for ET determination:
- Direct methods:
- Lysimetric method
- Water balanced method
- Soil moisture depletion method
- Field experimental plot method
- Indirect methods:
- Pan evaporimeter method
- Modified penman method
- Blanney Criddle method
- Thornthwaite method
- Christiansen method
- Radiation method
Lysimetric method for the ET determination with precaution
Lysimetric method for ET determination:
Lysimetric is a large container or pan used for growing crops. The pan may be metallic, bricks RCC made, water type container and placed in the soil.
The size of the tank maybe 1m × 1m × 1m.

At the bottom of the tank, there is a hole covered by a screen and connected with a discharge tube which is terminated to a container kept in the collection chamber. A ladder is set up in the collection chamber.
The lysimetric is placed in the crop field with the same soil level and also used for the same crop.
Calculation: Let, Water added = Q cm3, Water collected = Q´ cm3, Time = t days
Therefore, ET loss = Q-Q´/t cm3/day
Rate of ET per unit area = Q-Q´ cm3/day/t ×cm²(area)
= Q-Q´/t cm/day
Precaution:
- The size of the lysimetric should be large enough and deep so that the normal growth and development of roots are not disturbed.
- The physical and chemical properties of soil should be the same both inside and outside of the lysimeter.
- The crops grown on lysimeter should be identical to the crop field and culture or management practices should be the same.
- Lysimeter should be placed in the middle of a large crop field (10 acres) having the same type of crop.
- Lysimeter must be a waterproof chamber.
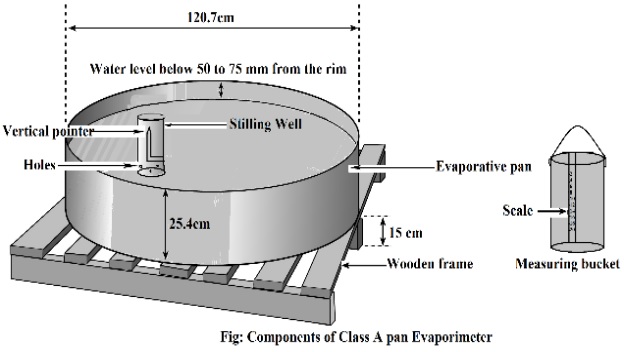
Evaporimeter method of ET measurement:
Pan evaporimeter an evaporimeter is a metallic pan made with a G.I. sheet. The height and diameter of the pan are 25 cm and 120 cm respectively. The pan is placed on a wooden frame, so that air can moves freely.
Firstly, about 20 cm of the pan is filled up with water. A hook gauge and a scale are adjusted here. The scale is set up in such a way that the hook touches the water surface.
The water level is decreased due to ET loss. Water is added again up to the former level. The water level is measured with the help of the hook gauge.
Reading:
Reading is taken at 6 – 8 AM and 7 – 8 PM daily. This is continued up to a certain period of 1 to 3 months. Then ET is measured.
By following formula, we know that,
Crop factor,
Kc = ET/PET
ET = Kc × PET , equation no 1.
Again, Pan factor,
Kp = PET/E
PET = Kp × E
From equation no 1 ,
ET = Kc × PET
ET = Kc × Kp × E
Here,
- Kc = Crop factor, (0.2 – 1.0)
- Kp = Pan factor (0.40 – 0.85)
- ET = Evapotranspiration
- PET = Potential evapotranspiration
- E = Evapotranspiration loss (cm/day)