 |
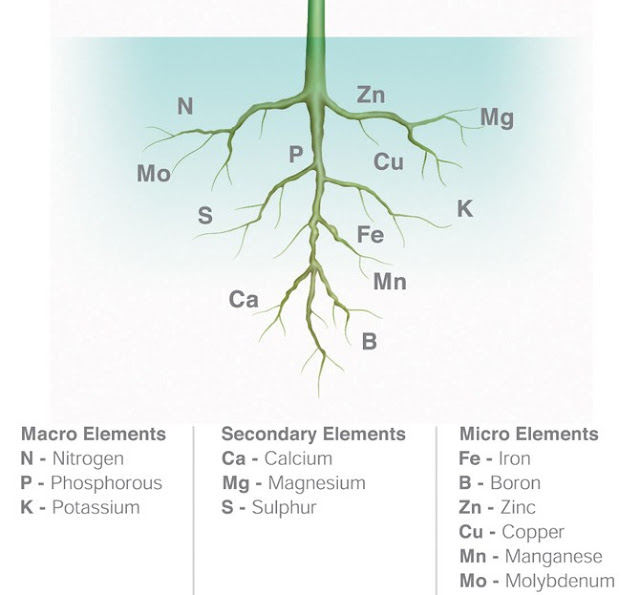
Role/function of essential plant nutrients
Deficiency of an element: When an essential element is at a low concentration in the plant tissues it will result in a decrease in normal growth of the plant, affect the crop yield, and produce more or less distinct deficiency symptoms.
* Typical deficiency symptoms are not often clearly defined. Masking effects due to other nutrients, secondary causes like disease, herbicide toxicity or insect infestation can confuse field diagnosis.
* Waterlogged conditions or dry soils and mechanical damage can often create symptoms that mimic deficiencies.
* Deficiency symptoms always indicate severe starvation.
Insufficient levels:When the level of an essential plant nutrient is below the required amount for optimum yields or when there is an imbalance with other nutrients it is considered insufficient. The symptoms of this condition are seldom clearly visible, resulting in poor yield.
Toxicity: Certain essential plant nutrients, if taken up in excess will often cause nutrient imbalances and will result in poor plant growth, delayed maturity, stunted and spindly growth and also show visible symptoms of chlorosis or necrosis.
Hidden hunger:There are no visual symptoms of deficiency but the plant is not producing at its capacity. When the plant reaches the level where symptoms appear, the yield may already have been greatly reduced. Identification of nutrient hunger signs is basic to profitable crop production.
Deficiency symptoms can be categorized into five types:
i. Chlorosis, which is yellowing, either uniform or interveinal of plant leaf tissue due to reduction in the chlorophyll formation.
ii. Necrosis, or death of plant tissue.
iii. Lack of new growth or terminal growth resulting in rosetting.
iv. An accumulation of anthocyanin and / or appearance of a reddish colour.
v. Stunting or reduced growth with either normal or dark green colour or yellowing.
If you can’t understand something please comment below…
